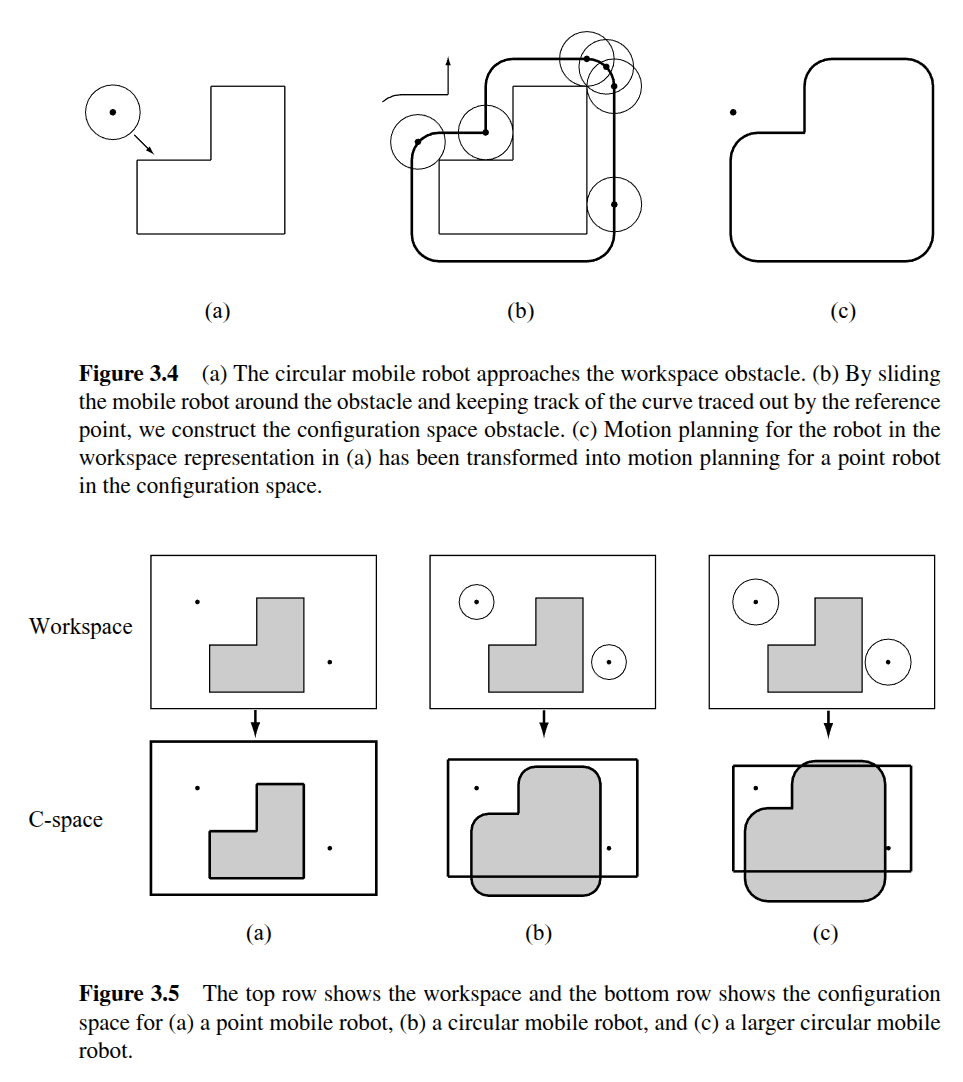
Let’s define a problem of determining a continuous mapping, such that no configuration in the path causes a collision between the robot and an obstacle.
A configuration space obstacle is defined to be the set of configurations where a robot intersects and obstacle in the workspace.
The free space is the set of configurations where the robot does not intersect any obstacles .
a free path is a continuous mapping .
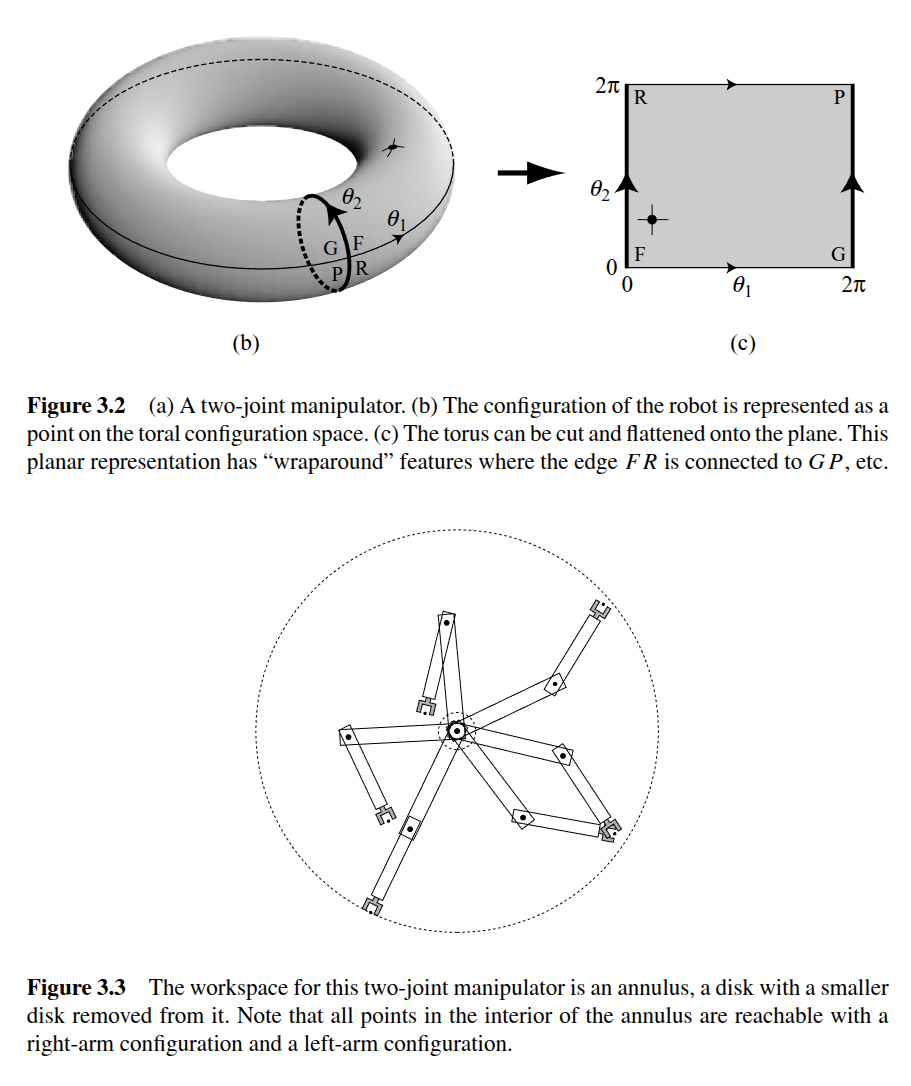
3.2.1 Circular Mobile Robot
Consider a robot that is a circle and has no rotational orientation. given some radius its configuration is easy to define around some (x,y) at its center point. Thus its configuration space is
There is a good visualization showing how c-space changes wrt. the robot, and how the workspace is different than the robot.
3.2.2 Two-joint Planar Arm
The two-joint arm has a different configuration space than the circular mobile robot, since its rigid links would self-collide in the center of the configuration. The two-joint arm’s configuration is a circle with a smaller circle cut out of the center - denoted .
Here is a visualization of the work space and the configuration space of a two link arm.