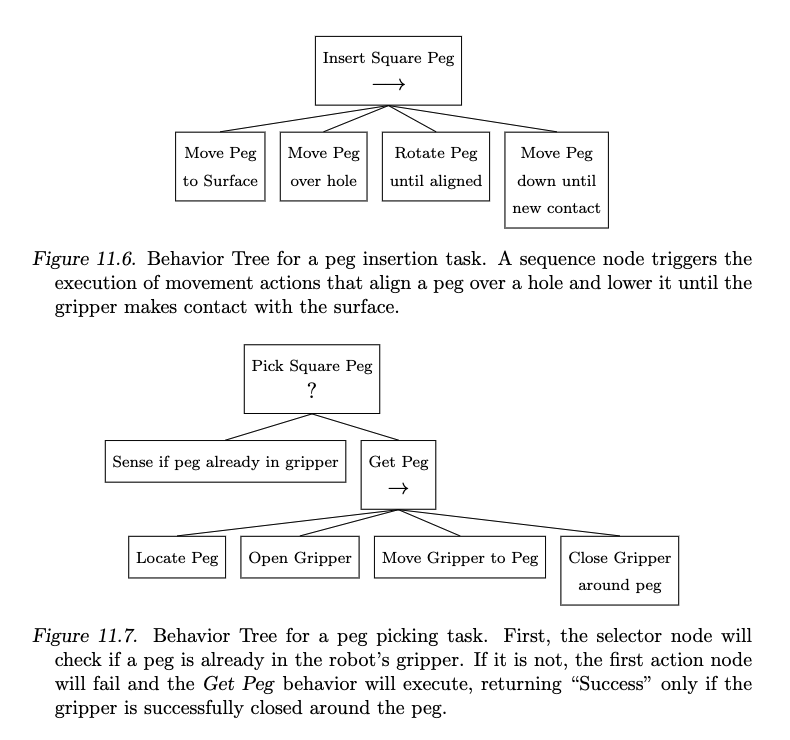
A Behavior tree is similar to a behavior flowchart - though not exactly.
Each Node has 3 potential states - “Success”, “Failure”, “Running”. Each Node can also be of a few types, namely composite, decorator, and action.
- composite nodes have one or more children and are responsible for refulating the control flow.
- decorator nodes have only a single child and perform transformations on its child node’s outputs back to its parents.
- An example is an inverter node - NOT “Success” or “Failure”.
- action nodes have zero child nodes and represent the execution of discrete behavior.
Each node’s children are all executed from left to right.